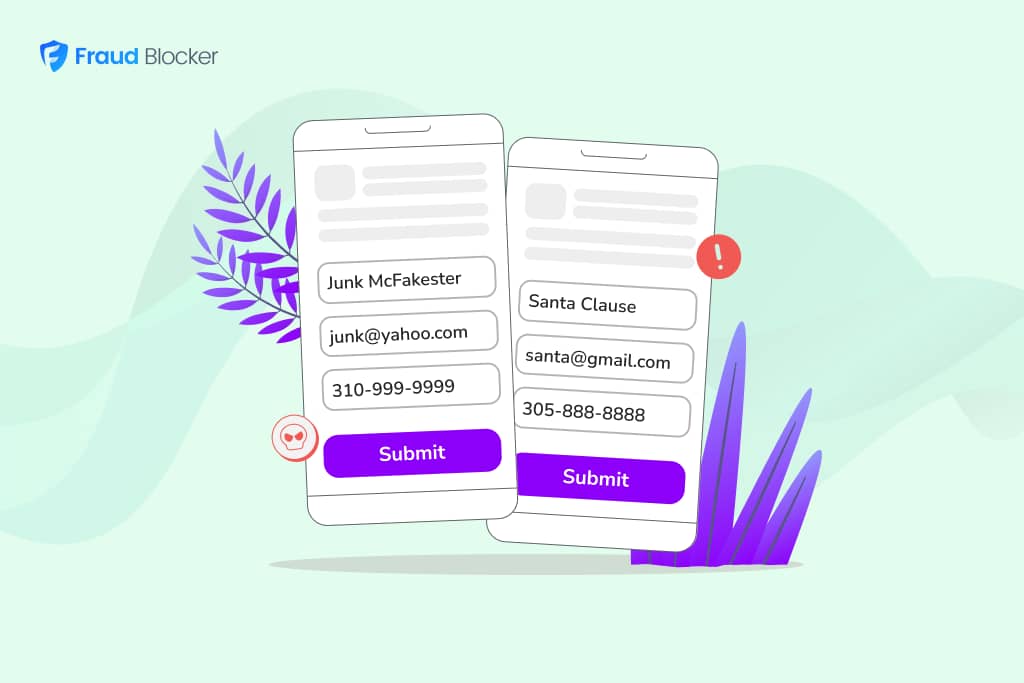
NEW New feature: Verify & block fake emails

We improve your ad performance by blocking click fraud and fake emails

Click fraud is costing advertisers billions in loses. Learn more here.

Click fraud is costing advertisers billions in loses. Learn more here.
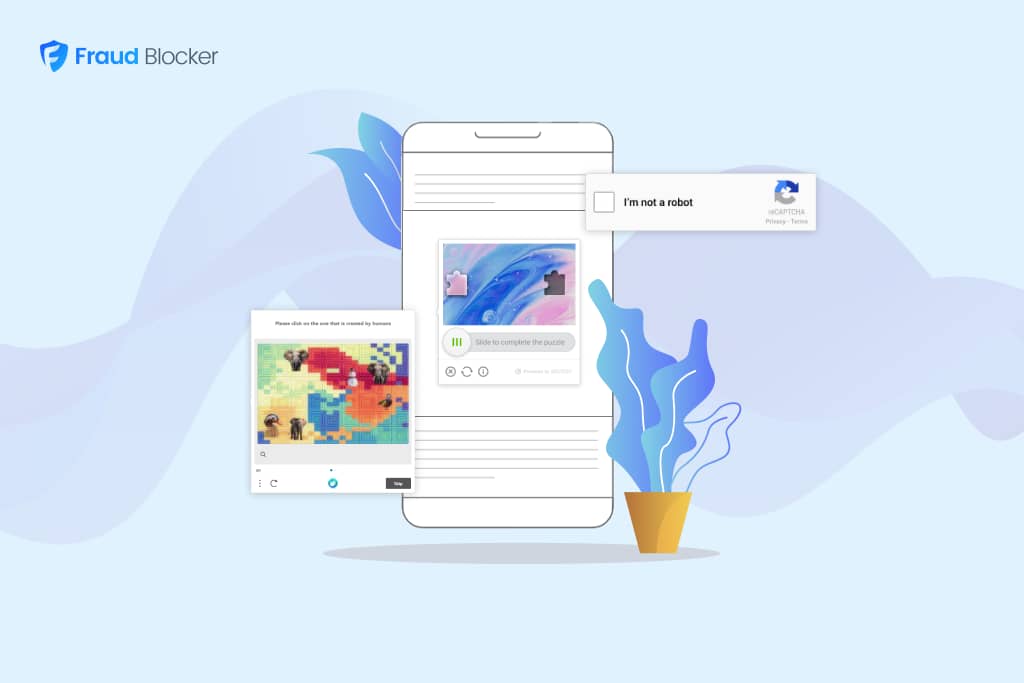
CAPTCHA is a challenge-response test used in computing to determine whether the user is human or not. This technology helps protect websites from spam and abuse by automated bots.
CAPTCHAs usually require users to complete tasks that are simple for humans but challenging for computers. Common examples include typing letters and numbers from a distorted image, identifying objects in a series of photographs (like selecting all images with traffic lights), or solving a basic math problem. These tasks are easy for humans to solve but difficult for automated systems, thereby providing a way to distinguish between the two.
CAPTCHA stands for the Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart.
CAPTCHAs come in various forms, each designed to test tasks that humans can easily perform but challenge automated bots. Here are some common types of CAPTCHA:
Text-based CAPTCHA: This is the most traditional form, where users are required to type letters and numbers that appear in a distorted image that often includes noise and line disruptions to prevent automated reading.
Image-based CAPTCHA: Users must select images that fit a certain description (e.g., “Select all images with cars”), helping to ensure that the responder is human.
Slide CAPTCHA: The user must slide a piece of an image into the correct position on the large image next to it.
Audio CAPTCHA: Useful for visually impaired users, this type involves playing an audio clip of distorted letters and numbers that the user must type correctly.
3D CAPTCHA: These involve identifying or manipulating three-dimensional objects, which adds an extra layer of complexity for bots.
Math CAPTCHA: This CAPTCHA asks users to solve a simple math problem, like addition or subtraction, which can be automated but when combined with other methods can increase security.
NoCAPTCHA reCAPTCHA: A simpler form for users, where they only need to check a box saying “I’m not a robot.” Advanced behind-the-scenes analysis of the user’s engagement with the CAPTCHA box and their interaction with the site is conducted to ensure they are human.
Biometric CAPTCHA: Some advanced systems use biometrics, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, though these are less common due to privacy concerns and technical requirements.
Each type of CAPTCHA offers different benefits and challenges and can be selected based on the specific security needs and user experience considerations of the website implementing them.
The primary purpose of CAPTCHA is to create tasks that are easy for humans but difficult for automated systems. However, advances in artificial intelligence, particularly in fields like machine learning and computer vision, have enabled some bots to bypass CAPTCHA protections.
Bots now complete CAPTCHAs more successfully than humans 😔, according to a recent study from Cornell University. This could potentially make the use of CAPTCHAs counterproductive by giving a false sense of security about the quality of your leads, which might actually be lower due to bot interference.
There are a number of software tools on the market that can help humans complete captcha but are usually exploited to help bots at a fraction of the time and speed. These include:
These CAPTCHA tools are the most popular on the market and do the best to prevent bots from completing them.
As you’ve read, bots are everywhere. They’re sophisticated and capable of doing a lot of harm. And it doesn’t stop with completing CAPTCHAs. 22% of ad spend is also lost due to bots clicking on your ads.
Fraud Blocker can help boost your ad performance by removing fraud, bots, accidental clicks, and more from your advertising campaigns. Try our 7-day free trial and see how much money we can save you.