What is Auto-Tagging in Google Ads?
Auto-tagging is a feature primarily associated with Google Ads. It automatically appends a parameter, the GCLID (Google Click Identifier), to your URLs when a user clicks on your ad. This process simplifies the tracking of user behavior and conversions directly from Google Ads. Auto-tagging is known for its ease of use, as it requires minimal setup and offers seamless integration with Google Analytics.
Why is Auto-Tagging important?
Auto-tagging is of paramount importance for businesses striving to remain competitive and adaptive. This technology automates the process of tagging each final URL, enabling businesses to swiftly identify trends and focus on aspects that are most relevant to their customer base.
A significant advantage of auto-tagging is the elimination of the need for manual tagging of each URL. Manual tagging is not only labor-intensive but also susceptible to errors. Auto-tagging circumvents these issues, ensuring a more efficient and accurate process.
Moreover, auto-tagging provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of ad clicks in driving customer actions, such as making purchases or completing sign-ups. This information is crucial for businesses to fine-tune their marketing campaigns, allowing for optimization of their investment returns.
In essence, auto-tagging is an indispensable tool for modern businesses, offering a strategic edge in understanding and engaging with their customer base.
What information does Auto-Tagging collect?
Auto-tagging appends your URLs with a special parameter called “gclid” (Google Click ID) that captures data for several additional dimensions, including:
- Campaign
- Source
- Medium
- Content
- Keyword
- Query Match Type
- Ad Group ID
- Final URLs
- Ad Format
- Ad Network
- Placement Domain
- Google Ads Customer ID
Auto-tagging also allows you to receive richer details on the data above including:
- Hour of Day
- Placements (Where your ads on the content network were placed)
- Display Targeting
- Video Campaigns
- Shopping Campaigns
How is Auto-Tagging different than UTM tagging?
UTM tagging, on the other hand, offers a more manual approach.
UTM parameters are tags that you add to the end of a URL. These tags can track just 5 of the parameters mentioned above:
source, medium, campaign, term, and content. But, unlike auto-tagging, UTM tagging is not limited to a single platform such as Google Analytics. It provides flexibility and detailed insights across various platforms, making it a versatile tool for marketers.
Auto-tagging example:
http://amazing-website.com/?gclid=12345abcf2
UTM tagging example:
http://amazing-website.com/?utm_source=google&utm_medium=cpc&utm_campaign=awesome-campaign&utm_term=cool-keyword&utm_content=creative
Learn more about UTM tracking.
Should I use Auto-Tagging or UTM tagging?
Both tagging methods have their merits.
Auto-tagging’s integration with Google Analytics is unrivaled, providing detailed and accurate data without additional configuration. Auto-tagging is highly efficient for tracking Google Ads campaigns. It eliminates the risk of human error in tagging and offers a streamlined process. However, its usage is confined to Google’s ecosystem.
UTM tagging, while more labor-intensive, offers broader applications. It allows for detailed tracking across different platforms, including social media, email marketing, and beyond. This versatility makes UTM tagging a valuable asset for a comprehensive digital marketing strategy.
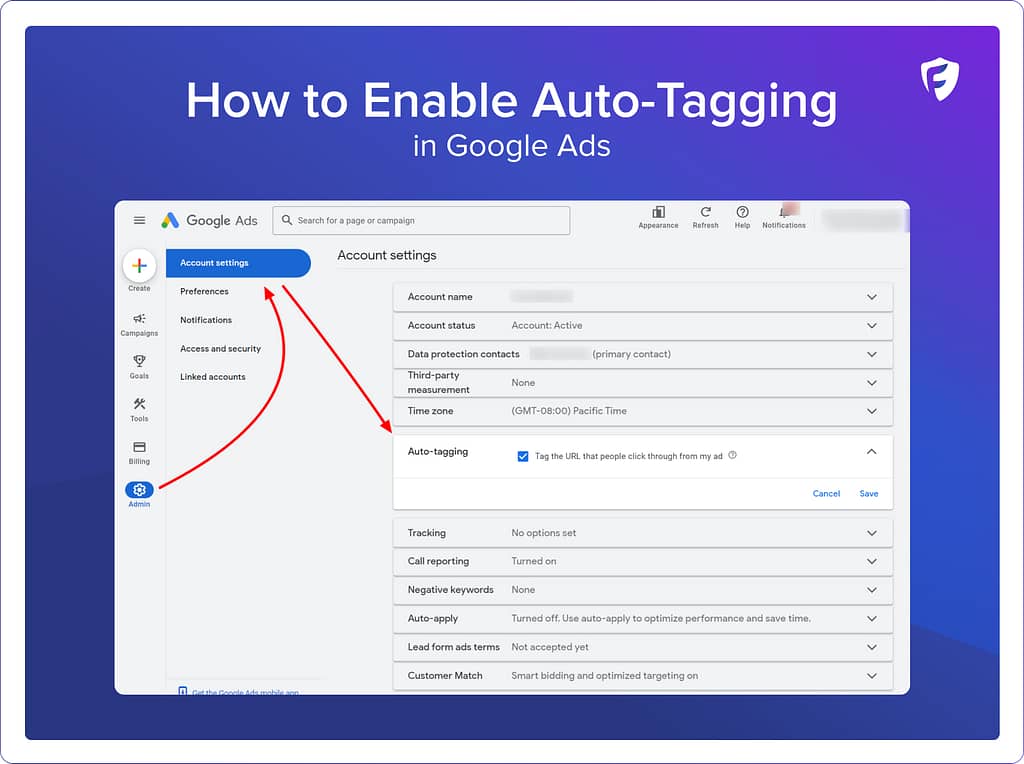
How do I turn on Auto-Tagging in Google Ads?
- In your Google Ads account, select the Admin icon.
- Select Account settings.
- Select Auto-tagging
- Auto-tagging is turned on by default. To turn auto-tagging off, click the box next to “Tag the URL that people click through from my ad”.
- Select Save.